پژوهشگران دانشگاه لیژ، و دانشگاه کاتولیک لوون بلژیک، دانشگاه بارسلون اسپانیا، دانشگاه بوستون و دانشگاه هاروارد ایالات متحده امریکا در پژوهشی مشترک به بررسی اثربخشی و تاثیر tDCS بر بیماران دارای آسیب مغزی شدید پرداختند.
روش:
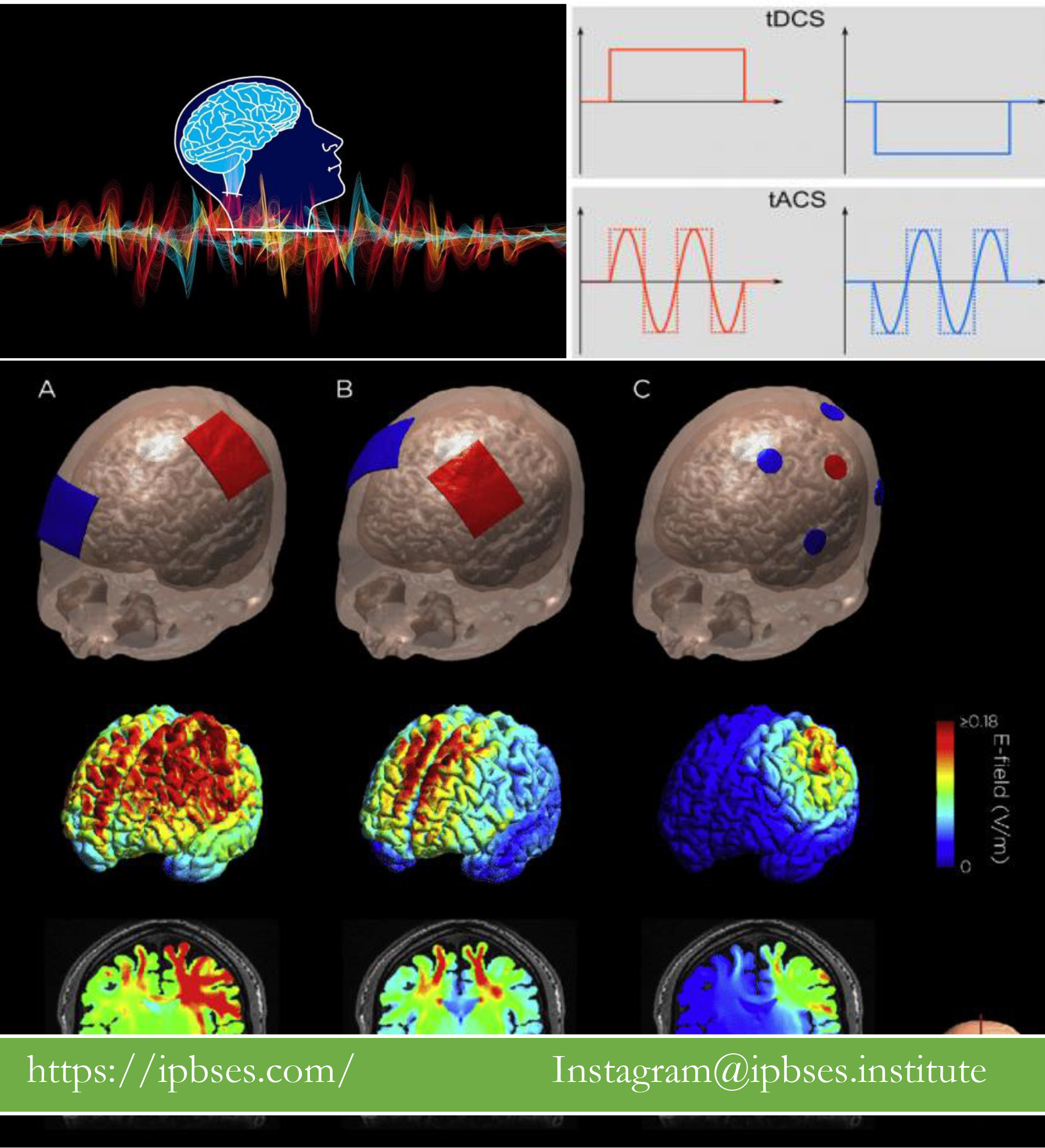
در این پژوهش ۴۶ بیمار بعد از کما بین ۱۶ تا ۷۵ سال که حداقل ۲۸ روز از تصادفشان میگذشت شرکت نمودند. در این پژوهش از tDCS چندکانونی با ۴ الکترود کاتدی و ۴ الکترود آندی به مدت ۲۰ دقیقه با شدت ۱ میلی آمپر استفاده شد. نوار مغزی و مقیاس سنجش بهبود از کما (CRS-R) پیش و پس از اجرای تحریک مغزی از شرکت کنندگان گرفته شد.
نتایج:
- در سطح گروهی، تاثیر tDCS بر بیماران دارای آسیب مغزی در حوزه رفتاری معنادار نبود.
- در سطح نوار مغزی (EEG) گروهی، تاثیر tDCS بر بیماران دارای آسیب مغزی شامل افزایش معنادار پیچیدگی نوار مغزی در باندهای با فرکانس پایین (۱ تا ۸ هرتز، دلتا و تتا) بود.
- افزایش نمرات شاخص بهبودی بعد از کما (CRS-R) همراه با کاهش پیچیدگی نوار مغزی در باندهای فرکانس پایین (۱ تا ۸ هرتز، دلتا و تتا) بود.
راهبردهای کارکردی:
- نتایج رفتاری تاثیر tDCS بر بیماران دارای آسیب مغزی حسب میزان آسیب به هشیاری آنها متفاوت است.
- نتایج الکتروفیزیولوژیک تاثیر tDCS بر بیماران دارای آسیب مغزی شدید در سطح نوار مغزی مشاهده شده ولی در سطح رفتاری تغییر خاصی نمودار نمیشود.
- تاثیر tDCS بر بیماران دارای آسیب مغزی شدید با وجود استفاده از چندین کانال الکترودی هنوز نامشخص است و در حال حاضر نمیتوان بعنوان پروتکلی پیشنهادی در درمان، آن را به کار برد.
Behavioral and electrophysiological effects of network-based frontoparietal tDCS in patients with severe brain injury: A randomized controlled trial
Abstract
Background
Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) may promote the recovery of severely brain-injured patients with disorders of consciousness (DOC). Prior tDCS studies targeted single brain regions rather than brain networks critical for consciousness recovery.
Objective
Investigate the behavioral and electrophysiological effects of multifocal tDCS applied over the frontoparietal external awareness network in patients with chronic acquired DOC.
Methods
Forty-six patients were included in this randomized double-blind sham-controlled crossover trial (median [interquartile range]: 46 [35 – ۵۹] years old; 12 [5 – ۴۷] months post injury; 17 unresponsive wakefulness syndrome, 23 minimally conscious state (MCS) and 6 emerged from the MCS).
Multifocal tDCS was applied for 20 min using 4 anodes and 4 cathodes with 1 mA per electrode.
Coma Recovery Scale-Revised (CRS-R) assessment and 10 min of resting state electroencephalogram (EEG) recordings were acquired before and after the active and sham sessions.
Results
At the group level, there was no tDCS behavioral treatment effect. However, following active tDCS, the EEG complexity significantly increased in low frequency bands (1–۸ Hz).
CRS-R total score improvement was associated with decreased baseline complexity in those bands.
At the individual level, after active tDCS, new behaviors consistent with conscious awareness emerged in 5 patients. Conversely, 3 patients lost behaviors consistent with conscious awareness.
Conclusion
The behavioral effect of multifocal frontoparietal tDCS varies across patients with DOC. Electrophysiological changes were observed in low frequency bands but not translated into behavioral changes at the group level.
Keywords
TDCS, Network, Minimally conscious state, Unresponsive wakefulness syndrome, EEG, Consciousness.
لینک منبع پیشنهادی برای مطالعه بیشتر  (further reading)
(further reading)